In the rapidly evolving world of cryptocurrency and blockchain technology, the concept of transaction fees has become a focal point of discussion and debate. Blockchain, the decentralized ledger technology that underpins cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum, relies on a network of nodes to validate and record transactions. To incentivize miners and secure the network, users are required to pay transaction fees. But what exactly are these fees, how do they work, and why are they so important in the world of blockchain? In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of blockchain transaction fees, shedding light on their significance, factors influencing their costs, and the implications they have on the broader cryptocurrency ecosystem.
What is the Purpose of Transaction Fees?
Transaction fees have constituted a fundamental component of virtually all blockchain systems since their inception. It’s highly probable that you’ve encountered these fees when engaging in activities such as sending, depositing, or withdrawing cryptocurrencies.


The utilization of transaction fees by the majority of cryptocurrencies serves dual pivotal purposes. Firstly, these fees serve as a mechanism for curtailing spam within the network, rendering large-scale spam attacks economically burdensome and impractical. Secondly, they function as an incentive for users who participate in the validation and verification of transactions, akin to a reward for their contribution to the network’s integrity.
While transaction fees on most blockchains typically remain cost-effective, they can escalate considerably based on network congestion. As a user, the extent to which you are willing to allocate funds for fees directly impacts the priority of your transaction in the queue for inclusion in the subsequent block. In essence, a higher fee equates to a faster confirmation process.
Bitcoin Transaction Fees
Being the pioneer in the realm of blockchain networks, Bitcoin established the prevailing standard for transaction fees, a practice widely adopted by numerous cryptocurrencies today. It was Satoshi Nakamoto who astutely recognized the dual role of transaction fees: safeguarding the network against large-scale spam attacks and offering incentives for positive user behavior.


In the Bitcoin ecosystem, transaction fees constitute a portion of the rewards received by miners during the process of validating transactions for inclusion in a new block. The reservoir of pending, unverified transactions is commonly referred to as the memory pool or mempool. In this context, miners naturally prioritize transactions that come with higher fees, which users willingly attach to their BTC transfers to other Bitcoin wallets.
Individuals with malevolent intentions seeking to impede the network’s operations are obliged to include a fee with each transaction they initiate. If they opt for an insufficient fee, miners are inclined to disregard their transactions. Conversely, if they set the fee at an appropriate level, it imposes a substantial economic burden on them. Therefore, transaction fees also function as a straightforward yet highly effective mechanism for filtering out spam.
What Is the Method for Determining Transaction Fees in Bitcoin?
Within the realm of the Bitcoin network, specific cryptocurrency wallets empower users with the capability to manually configure their transaction fees. It is also worth noting that it is feasible to transmit BTC without attaching any fees; however, it is highly probable that miners will disregard such transactions, thus rendering them unverified.
Contrary to a common misconception, the fees associated with Bitcoin transactions do not hinge on the amount being sent but rather on the size of the transaction, measured in bytes. To illustrate, consider a scenario where the transaction size amounts to 400 bytes, and the prevailing average transaction fee stands at 80 satoshis per byte. Under these circumstances, one would need to remit approximately 32,000 satoshis (equivalent to 0.00032 BTC) to significantly enhance the chances of their transaction being promptly included in the subsequent block.
In instances where network congestion is substantial, coupled with heightened demand for BTC transfers, the transaction fee required for expedited confirmation escalates, as numerous Bitcoin users vie for the same objective. Such situations are apt to arise during periods marked by intense market fluctuations.
Consequently, the elevated fees can present a challenge when attempting to utilize BTC for everyday transactions. For instance, acquiring a $3 cup of coffee may become impractical if the fees surpass this modest amount.
It’s essential to recognize that each block, subject to a 1MB size limit, can only accommodate a limited number of transactions. Miners endeavor to append these blocks to the blockchain as expeditiously as possible, yet there remains an intrinsic constraint on their processing speed.
The issue of scalability holds considerable significance in determining network fees within the realm of cryptocurrency networks. Blockchain developers are tirelessly working towards addressing this challenge. Previous network upgrades, such as the implementation of Segregated Witness (SegWit) and the Lightning Network, have played pivotal roles in enhancing scalability.
Ethereum Transaction Fees
Ethereum transaction fees operate in a distinct manner when contrasted with Bitcoin’s fee structure. These fees factor in the computational resources required for transaction processing, which are quantified as ‘gas.’ Gas, in turn, has a variable cost denominated in ether (ETH), Ethereum’s native cryptocurrency.


Although the gas required for a particular transaction may remain constant, gas prices exhibit fluctuations, influenced by network congestion. Opting for a higher gas price is likely to result in miners giving precedence to your transaction.
What Is the Method for Determining Transaction Fees in Ethereum?
The total gas fee can be thought of as a composite value encompassing not only the cost of the transaction but also an added incentive for processing your transaction efficiently. It’s important, though, to take into account the gas limit, which sets an upper threshold on the price you’re willing to pay for a specific transaction or task.
To put it differently, the gas cost represents the quantum of work that needs to be accomplished, while the gas price signifies the price you’re willing to pay for each unit of work performed, akin to an hourly wage. The interplay between these two factors, along with the gas limit, ultimately determines the overall fee associated with an Ethereum transaction or a smart contract operation.
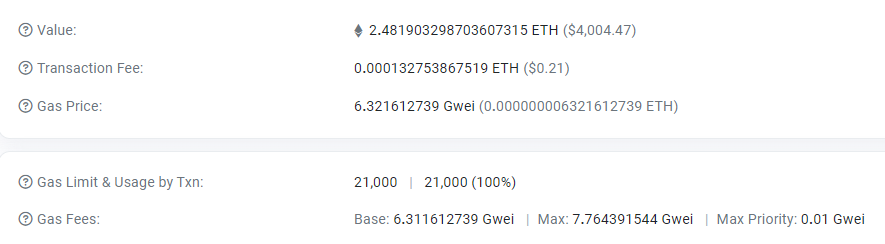
Let’s illustrate this with a random transaction from Etherscan.io as an example. The transaction, in this case, consumed 21,000 units of gas, and the gas price was set at 6.32 Gwei. Consequently, the total transaction fee amounted to 0.0001327 ETH.

Conclusion
Transaction fees play a crucial role in the crypto economics of blockchain networks, constituting an essential component of the incentives provided to users for sustaining network operations. These fees also serve as a protective barrier against malicious activities and spam.
Nevertheless, the surging levels of network traffic experienced by certain blockchain networks have resulted in notably elevated transaction fees. The inherent decentralized nature of most blockchains introduces challenges in terms of scalability. While some networks do exhibit commendable scalability and transaction throughput, these attributes often entail trade-offs in either security or decentralization.
Nonetheless, there exists a dedicated community of researchers and developers diligently working on innovations with the potential to foster greater accessibility to cryptocurrencies in the developing world.











