The way individuals perceive and utilize cryptocurrencies has evolved significantly since the advent of decentralized finance (DeFi). This shift has been particularly notable with the emergence of independent financial platforms offering various types of crypto lending, which, in turn, create substantial value for both borrowers and lenders alike.
One specific type of loan that has experienced a remarkable surge in popularity within the DeFi ecosystem is the flash loan. Flash loans offer borrowers the opportunity to capitalize on arbitrage opportunities in a matter of moments. These loans provide the necessary funds to purchase a crypto asset, quickly sell it, repay the loan, and generate a profit—all within a single transaction.
However, despite the brilliance of the concept and its effectiveness in practice, there are unfortunately individuals who exploit this form of lending. Continue reading to discover more about flash loan attacks and how to safeguard against them.
What Is a Flash Loan Attack?
A flash loan attack involves the exploitation of vulnerabilities in the smart contract security of a specific platform. In this type of attack, the perpetrator typically borrows a substantial amount of funds without needing to provide any collateral. The attacker then proceeds to manipulate the price of a cryptocurrency on one exchange, artificially inflating or deflating its value, and quickly resells the asset on a different exchange to profit from the price difference.


This entire process occurs in a rapid sequence of events, often happening within the same transaction. The attacker repeats this manipulative cycle multiple times in quick succession before finalizing the operation and disappearing without leaving any traceable evidence behind.
What Is a Flash Loan?
The rapid development of the decentralized finance (DeFi) lending sector has significantly contributed to the growing popularity of crypto lending. Flash loans, in particular, have emerged as an especially attractive option because they harness the full potential of current blockchain technologies.
A flash loan allows a borrower to obtain a loan without the need for collateral. But how is this possible? By utilizing a platform’s smart contract, the entire lending and repayment process is executed within a single transaction on the blockchain.
This means that the borrower must act swiftly, ensuring the loan is repaid within a very short time frame. If any part of the process fails—such as the borrower defaulting—the transaction is automatically nullified, as though it never took place.
The concept is both straightforward and highly efficient. Unlike traditional secured loans, flash loans don’t require any collateral, credit checks, or administrative procedures. Borrowers can instantly access large amounts of stablecoins, using them for their intended purposes just as quickly.
This is precisely what some traders on various DeFi platforms are doing. For instance, users on platforms like Aave can obtain flash loans, capitalize on arbitrage opportunities, repay the loan, and pocket the profits.
The system automates the entire borrowing and lending process, and when executed successfully, both the lender and borrower benefit from the transaction. However, if anything goes awry, the system cancels the transaction, leaving both parties without any profit.
How Frequent Are Flash Loan Attacks?
Due to the rapidly evolving nature of blockchain technology, DeFi flash loan attacks remain prevalent. To date, more than 70 DeFi exploits have been leveraged to steal vast sums of money, with losses totaling approximately $1.5 billion. This trend is likely to persist in the coming years, as achieving impenetrable security in DeFi platforms remains an ongoing challenge.
One of the primary difficulties lies in developers’ inability to anticipate every possible vulnerability, especially since blockchain is a relatively new field. Additionally, the rapid pace at which these systems are built, coupled with the substantial financial stakes involved, creates further complexity. With large sums of money on the line, developers often experiment with various methods to uncover potential flaws. Some flash loan attackers exploit miscalculations in liquidity pools, while others take advantage of coding errors or execute miner attacks.
Unfortunately, the very thing that makes decentralized finance possible—smart contracts—also introduces vulnerabilities.


The issue with smart contracts is that they have complete authority over DeFi protocols. Once attackers gain a deep understanding of how these contracts function, they can exploit their weaknesses to carry out attacks.
This creates a delicate balance in DeFi security: on one side, the skill and expertise of the protocol’s contract developers, and on the other, the hackers seeking to exploit any gaps.
Another significant vulnerability involves the platform’s pricing data. Given the numerous exchanges around the world, establishing a single, definitive price for crypto assets is nearly impossible. These pricing discrepancies make arbitrage trading attractive, as traders can legitimately profit from natural market fluctuations. However, flash loan attackers manipulate these price differences by triggering sudden and artificial shifts in value.
When an attacker secures a flash loan, they often orchestrate a fabricated sell-off, causing the price of a crypto asset to plummet.
Fortunately, there are already measures in place to mitigate the risk of such abuses with uncollateralized loans. We will examine some of these protective systems after discussing a few notable examples of flash loan attacks.
Examples of Flash Loan Attacks
Over the years, there have been numerous instances of flash loan attacks, with several standing out as particularly significant. Below are some of the largest attacks:
Cream Finance
C.R.E.A.M. Finance faced multiple attacks throughout 2021, with one of the most notable heists amounting to a staggering $130 million. The attackers managed to steal millions in CREAM liquidity tokens over an unspecified period. All the losses were recorded on-chain, but the culprits remain at large.
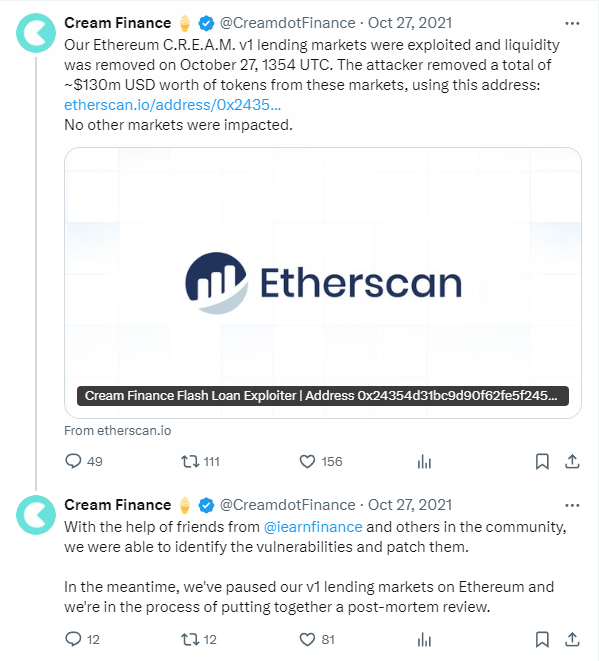

Fortunately, the vulnerability only affected a portion of Cream’s DeFi infrastructure, as its merging partner, Yearn Finance, remained unaffected. As is typical with DeFi protocol exploits, the attackers deployed multiple flash loans and manipulated the oracle’s price feed.
With the assistance of Yearn’s team, the vulnerability was swiftly patched.
dYdX
Some protocol exploits hinge on precise timing and price manipulation, as seen in the dYdX flash loan exploit in early 2020. The attacker took out a flash loan on the platform, then split the funds across two trading platforms — Fulcrum and Compound.
On Fulcrum, the first portion was used to exchange ETH for WBTC, with the order being routed through Uniswap’s DEX via the Kyber Network. Uniswap’s relatively low liquidity pool at the time caused WBTC prices to skyrocket.
Meanwhile, the attacker used the second portion of the loan on Compound to secure a WBTC flash loan. As the WBTC price surged on Uniswap, the attacker quickly executed the exchange, securing a substantial profit through price manipulation.
Alpha Homora
In February 2021, the Alpha Homora protocol was hacked, resulting in a $37 million loss. The attacker utilized C.R.E.A.M. Finance’s Iron Bank by executing a series of flash loans. The Iron Bank serves as the lending division of Alpha Homora.
The hackers repeated the exploit several times, accumulating CreamY USD (cyUSD) tokens, which were then used to borrow various cryptocurrencies. The attack was highly sophisticated, involving multiple steps. Essentially, the hacker manipulated the sUSD pool of HomoraBank v2 to their advantage.
By orchestrating a series of transactions and flash loans, the attacker was able to exploit the lending mechanisms between HomoraBank v2 and the Iron Bank. For a deeper dive into the incident, the Alpha Homora post-mortem details the hackers’ approach.
Additionally, the exploit leveraged a rounding miscalculation in the borrowing calculations, particularly in scenarios with a single borrower.
PancakeBunny
In May 2021, PancakeBunny was subjected to a devastating attack, with the hacker making off with nearly $3 million. The attacker began by taking out a large BNB loan through PancakeSwap. During the exploit, they manipulated the BUNNY/BNB and USDT/BNB trading pairs.
A subsequent flash loan allowed the hacker to amass a significant amount of BUNNY tokens, which were swiftly dumped. The hacker repaid the BNB loan and vanished with the profits. This attack caused PancakeBunny’s price to plummet dramatically, dropping from $146 to just $6.17.
How Can I Protect Against a Flash Loan Attack?
As the number of attacks continues to rise, security experts are gaining deeper insights into the numerous flash loan exploits that are emerging in the crypto space. Fortunately, all the vulnerabilities highlighted in the examples provided above have been successfully patched. Moreover, the recurrence of these issues has led to the development of two widely recognized solutions aimed at enhancing security in this area.
Deployment of DeFi Security Solutions
The DeFi ecosystem is utilizing state-of-the-art technologies that are fundamentally transforming the landscape of global financial systems. However, this heightened focus brings significant challenges and strains on the entire system.
Fortunately, there are already dedicated platforms designed to address the pressing security issues that arise in this environment. OpenZeppelin stands out as an exemplary case, playing a crucial role in safeguarding smart contracts and the broader DeFi platforms.
In addition to its smart contract auditing capabilities, solutions like Defender Sentinels offer continuous protection against flash loan attacks. This innovative tool allows developers to automate their defensive strategies, enabling them to swiftly pause entire systems and implement necessary fixes.
Such rapid response mechanisms are vital for minimizing the potential damage that a flash loan attack can inflict on the system.
Major players in the industry, including Yearn.finance, Foundation Labs, dYdX, Opyn, The Graph, PoolTogether, and many others, are already leveraging this platform to effectively neutralize attacks on their systems.
Decentralized Price Oracles
Most flash loan attacks heavily rely on price manipulation, making it crucial to combat this tactic with decentralized pricing oracles. Notable examples of such oracles include Chainlink and Band Protocol. These platforms enhance the security of various protocols by providing accurate and reliable pricing information for a range of cryptocurrencies.
For instance, decentralized finance (DeFi) attacks similar to the incident that occurred with dYdX will become less feasible, as protocols will no longer depend on a single decentralized exchange (DEX) for their price feeds.
Alpha Homora has now adopted the Alpha Oracle Aggregator to avoid a recurrence of past vulnerabilities. As the DeFi market continues to expand, we can expect to see more systems designed with this level of protection.
Are Flash Loans Risk-Free?
When everything operates as intended, flash loans can be regarded as completely risk-free. Both the borrower and the lender stand to gain from the transaction, provided that they adhere to all the conditions outlined in the smart contract.
From the lender’s perspective, they are never actually relinquishing any money. Instead, the funds are essentially virtual, becoming part of the blockchain ledger if the borrower fulfills all requirements. If the borrower defaults, the transaction is simply rejected, and the funds remain intact.
This means that the lender retains their assets, and the borrower does not incur any debt to anyone.
On the flip side, the borrower has the opportunity to realize a profit. They can utilize the borrowed funds to capitalize on arbitrage opportunities within the cryptocurrency market. If the transaction fails, the money seamlessly reverts to the lender.
Ideally, the system facilitates risk-free, instantaneous borrowing and lending. However, to truly ensure that the process is devoid of risk, the smart contracts must comprehensively cover all transaction details. This thoroughness eliminates vulnerabilities attackers could exploit.
Consequently, the most significant risks currently facing the DeFi ecosystem regarding flash loans are data leaks and bugs within smart contracts that could enable such attacks.
While the situation isn’t perfect now, there’s hope these systems will evolve to become secure. With platforms like Chainlink and OpenZeppelin involved, flash loan attacks may eventually become obsolete.
Conclusion
Flash loans represent an exciting and innovative addition to the decentralized finance (DeFi) ecosystem. Although they are currently vulnerable to various attacks, we anticipate that this situation will improve over time.
As developers continue to enhance their smart contract programming skills and as more systems implement robust security tools and decentralized oracles for accurate pricing, we can expect a notable decline in the frequency of attacks perpetrated by hackers.
If you’re contemplating whether flash loans constitute a wise investment opportunity, we firmly believe the answer leans toward yes. However, it’s important to keep in mind that there is, at the very least, a minimal risk associated with flash loan attacks. Therefore, exercise caution and be judicious when using your cryptocurrencies for lending on DeFi platforms.











